What is The Difference Between LED and Laser?
Currently, a wide variety of laser therapy devices have emerged in the animal/pet medical community. Some of them are indeed lasers, while others are not (they may be: infrared, ultraviolet, or LED lights). Laser, also known as laser beam, has the English name Laser. Many doctors feel uncertain when choosing laser equipment that suits their clinical needs. Vaymed will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the difference between laser and LED lights from the following four aspects:
-
1. Consistency of Light Direction
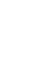
High-quality laser equipment is amplified by stimulated emission of light, with synchronous photon energy and consistent emission direction. This foundation allows the laser energy to penetrate deeper, more easily reaching deep tissues rather than being reflected, refracted, or scattered too quickly and excessively upon contact with the skin surface. The divergence of the class 4 laser has an extremely small divergence of approximately 0.001 radians, approaching parallel light rays. If properly controlled, most of the light energy can be incident ontothe treatment plane vertically, thereby reducing the proportion of light energy reflected. For example, when treating deep muscle injuries, the high directionality of the laser enables it to concentrate energy on deep tissues, improve treatment efficiency, and reduce the number of treatments. The divergence of infrared LED beams is relatively large, and there will be a certain cross angle between the light and the light, so it is difficult to make all the light incident on the treatment plane vertically. This causes more light energy to be reflected back, reducing the effective photon energy. In actual clinical applications, this means that LED phototherapy is less effective in treating deep-tissue diseases and is more suitable for superficial lesions.

-
2. Coherence of Light
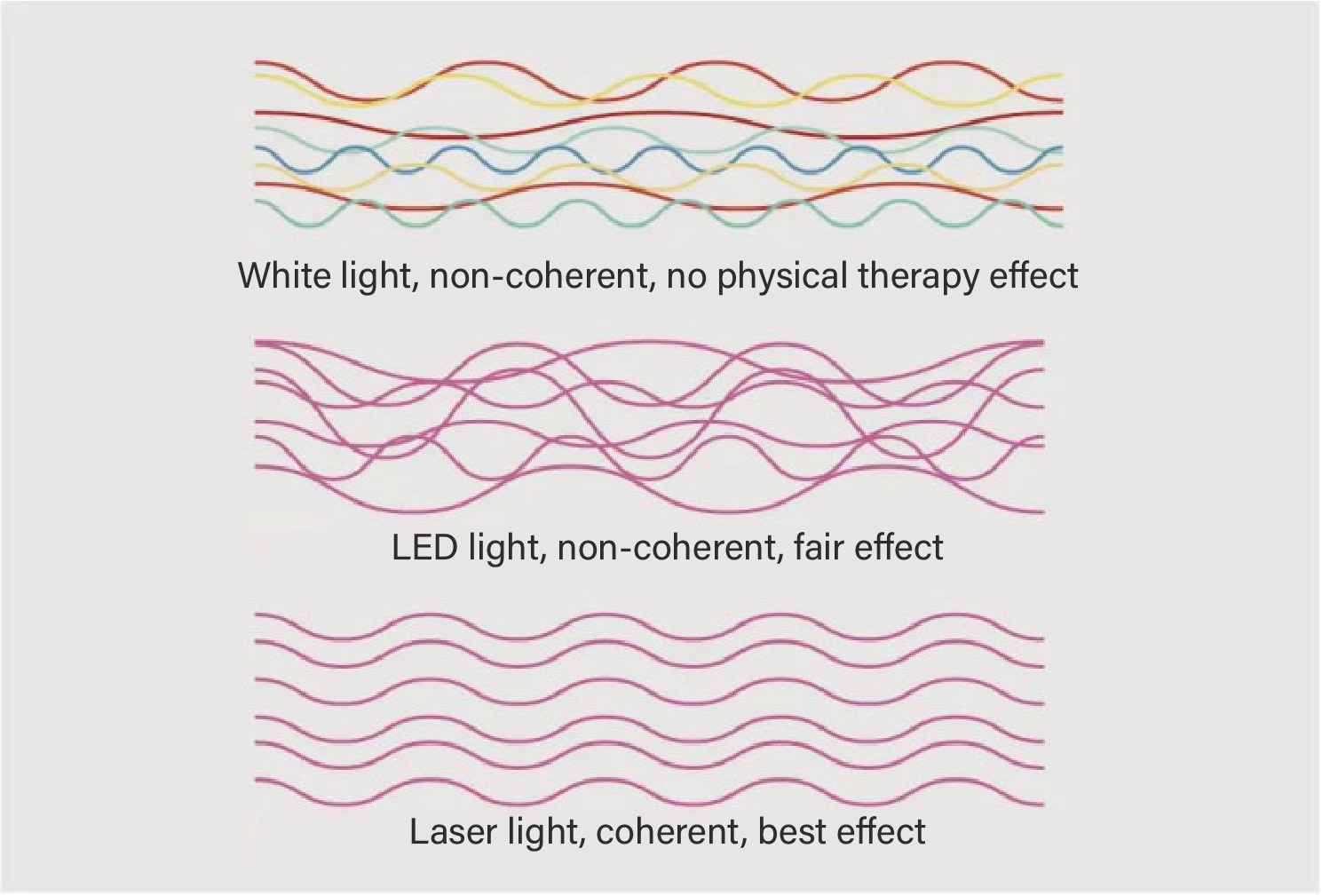
In order to increase the power of their products, some manufacturers install multiple LED bulbs around the laser to emit incoherent wavelengths. This has a certain effect on mucous membranes, wounds and very superficial conditions, but it is very limited. The photon energy of LEDs cannot reach deep tissues.. For white light (such as natural light, LED light, etc.), incoherent light is emitted, and there is no synergy between the wavelengths and little therapeutic effect. For coherent light (laser), coherence is crucial for successful treatment. All wavelengths are emitted at the same time and coherence is maintained for optimal therapeutic effect. In practical treatment, the coherence of the laser allows them to precisely target the lesion site, stimulatingthe photobiological effect in the cells, and promotingtissue repair and regeneration. For example, in the treatment of nerve injuries, the coherence of the laser ensures that the light energy is effectively absorbed by nerve cells and promotes the recovery of nerve function. However, due to the lack of coherence, LED light is dispersed, anddifficult to reach deep tissues, limiting its therapeutic effect on deep lesions.
-
3. Laser Power Density
The laser's divergence angle is generally very small, only about 0.001 radians, while the infrared LED light source divergence angle is larger. The larger the dispersion angle of the light source, the larger the photon energy diffusion area. The World Association for Laser Therapy (WALT) has defined the standard unit of the clinical dosage in laser therapy as the energy density, therefore, Class IV laser light source can achieve a higher photon energy density to reach the patient's treatment area in a shorter period of time. This feature is particularly important in deep treatment areas such as musculoskeletal and nerve. In practical applications, the high power density of lasers allows them to deliver large amounts of energy in a short period for rapid relief of pain and inflammation. For example, in the treatment of chronic muscle pain, laser therapy can often provide significant relief within a few treatments, while LED light therapy may require more treatments to achieve similar results.

-
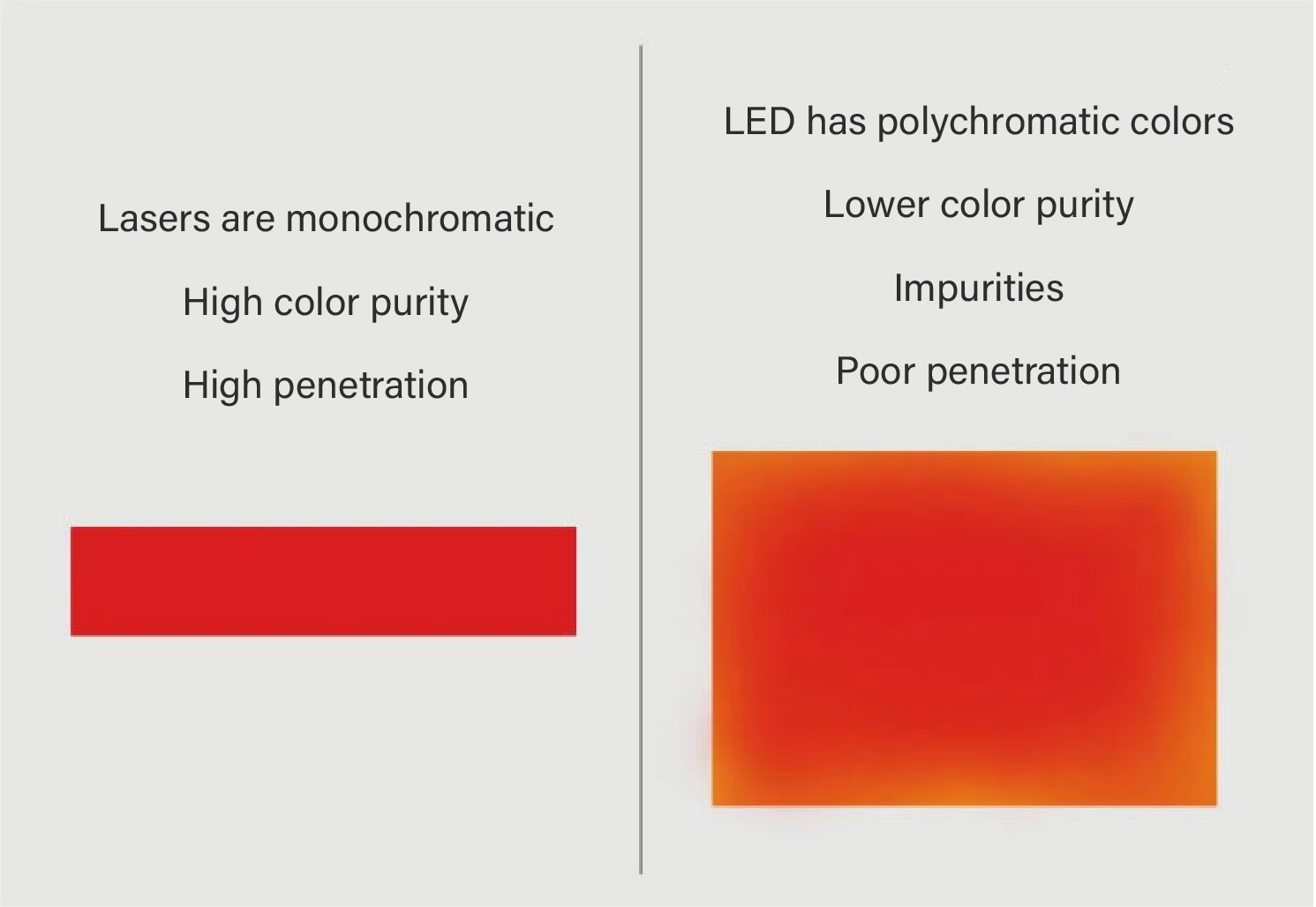
4. Wavelength Purity
The wavelength of the Class IV laser is characterized by monochromaticity, and the spectrum width is generally within 1~10nm. The color purity is extremely high and the wavelength is stable. The LED light source spectrum is generally wider, usually within the range of 25~100nm. Laser TV using high wavelength purity laser as the three primary colors has a wider color gamut space. That's why laser TVs have more brilliant colors than LED TVs. In medical clinical applications, specific wavelengths of photons play different roles in photobiomodulation (PBM). The more wavelength “impurities” are present in the light source, the more limited the therapeutic effect is. Therefore, a Class IV laser with higher wavelength purity is more efficient in utilizing light energy. In practical treatment, the high wavelength purity of laser enables it to precisely stimulate specific photobiological effects, improve the utilization efficiency of light energy, and enhance the therapeutic effect. For example, in treating skin ulcers, the specific wavelength of the laser can effectively promote the growth of granulation tissue and angiogenesis, accelerating wound healing. However, due to the wide wavelength and the presence of more "impurities", the role of LED light sources in treatment is relatively limited.