What is the Difference Between Class 3B Laser and Class 4 Laser?
Currently, there is a wide variety of laser therapy devices available on the market. These devices differ significantly in terms of wavelength, power, and operational specifications, such as continuous wave, pulsed wave, and super-pulsed modes. Although all these devices can achieve certain clinical effects to some extent, they vary greatly in terms of healing speed and treatment outcomes. Therefore, it is crucial to accurately understand the characteristics of different laser therapy devices. By delving into these differences, we can select the most suitable laser therapy device based on specific clinical needs and treatment goals, thereby ensuring the best possible therapeutic results.
Understanding Laser Classification
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) categorizes lasers as Class 1 (harmless in normal use) to Class 4 (significant risk from direct eye or prolonged skin exposure) based on the potential risk they pose to exposed individuals. This article focuses on the differences between Class 3B laser and Class 4 laser. Class 3B lasers pose a significant risk to the eyes and can cause serious eye damage from looking directly into the beam or from specular reflections. Generally, they do not cause thermal damage to the skin, but high-power Class 3B lasers can also burn the skin. When operating a Class 4 laser, animals and veterinarians must wear professional laser glasses because Class 4 lasers can cause permanent damage if they are directed at the eye, and prolonged exposure to the same part of the body, especially at the focusing spot, where the energy is highly concentrated, is likely to cause skin burns and serious tissue damage.
Differences Between Class 3B Laser and Class 4 Laser
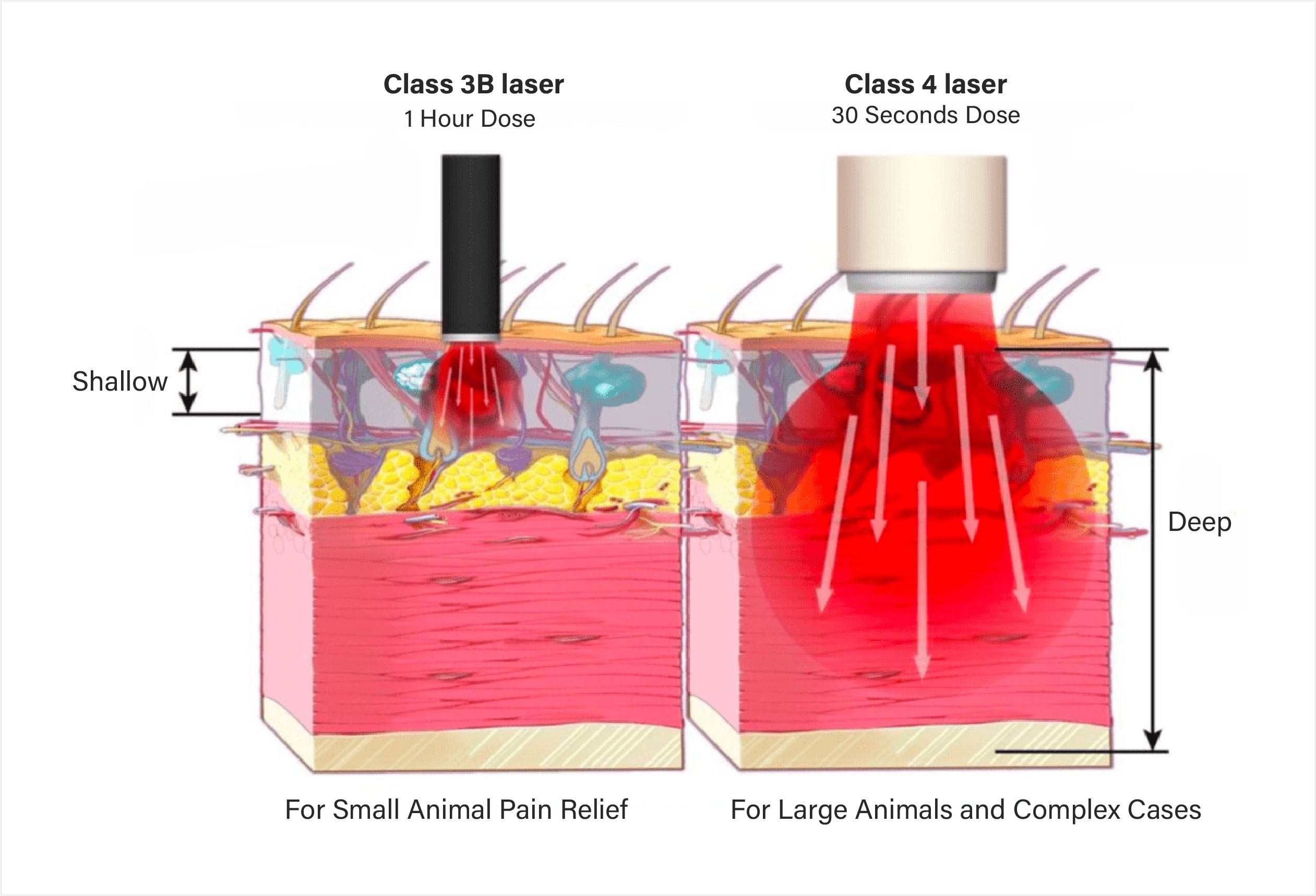
Power: The FDA limits the output power of Class 3B lasers to 500mW, while Class 4 lasers range from 500mW to 15W and higher. Higher power allows the veterinarian to treat a larger area in less time, delivering more energy to the diseased tissue, and resulting in faster healing with better therapeutic outcomes. For instance, the Vaymed Skyline Class 4 laser therapy equipment has a power output of up to 30 W and a tissue penetration depth of up to 15cm, making it one of the most popular laser physiotherapy devices on the market today due to its portability and excellent therapeutic results.
Tissue Penetration Depth: The penetration depth of a laser is influenced by its wavelength, power, as well as the tissue characteristics of the affected area. When the laser wavelength is within the therapeutic window, the higher the power, the deeper the penetration. Since Class 4 laser has higher power than Class 3B laser, they achieve greater penetration depth. In tissues with high water content (such as muscles or edematous areas), the penetration of the laser may be somewhat limited. In comparison, Class 4 laser therapy is more effective for deep wounds and is particularly suitable for treating large animals.
Treatment Strategy: Class 3B laser typically treats smaller areas and remains fixed on a single spot during treatment, whereas with class 4 laser treatment, the area treated is larger than the actual wound area and extends 2-5 cm beyond the wound edge. During class 4 laser treatment, contact or non-contact treatment is used, with the laser sweeping up and down in an S-shape or in a circular pattern, at a constant speed of 3-5 cm per second, to ensure even distribution of energy across the entire treatment area.
Dose Strategy: Class 3B laser therapy delivers relatively lower doses of Joule energy to smaller tissue areas, resulting in variable clinical outcomes. In contrast, Class 4 therapy laser reduces this variability by delivering therapeutic doses of Joule energy to large areas of targeted tissue. For example, a Class 4 laser device can deliver sufficient energy to the treatment area in less than 5 minutes, while a Class 3B laser would more than 16 hours to achieve the same energy delivery. This means that pets undergoing Class 4 laser therapy can experience faster pain relief and functional recovery.
Application Scenarios: Class 3B lasers are commonly used in areas where medium-power lasers are required, such as certain medical devices, industrial lasers, and 3D printers. In the medical field, they are primarily used for non-invasive treatments or diagnostic procedures. While Class 4 lasers are mainly used in specialized fields such as industry, scientific research, military, and medicine. In the industrial field, they are used for cutting, welding, and cleaning, etc; in scientific research, they are suitable for experimental studies and spectroscopic analysis; in the military, they are used for laser weapons and ranging, etc; and in the medical field, they are used for high-energy laser surgeries.
What Is the Corresponding Depth of Penetration for Different Powers of Class 4 Laser Therapy Equipment?
There is no fixed relationship between laser power and penetration depth; the depth of penetration varies within a certain range for different tissues. For example, for muscle tissue, a higher power is required for the same depth of penetration. The depth of penetration is 1-2cm at a laser power of 5W, 3-5cm at 10W, about 7-10cm at 15W, and can reach 12-15cm at 30W.
Why Is Wavelength Important in Laser Therapy?
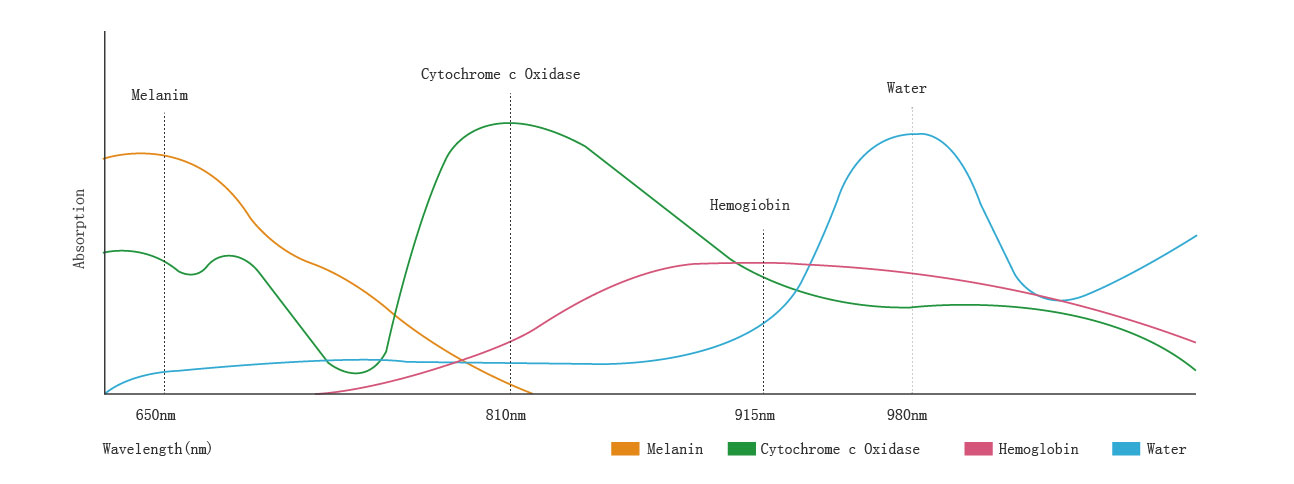
In view of the widespread use of laser therapy, which is able to cover about 80% of clinical diseases, it is particularly significant in the treatment of various inflammatory diseases and pain relief. In this regard, the penetration depth of a laser is not only influenced by power, but the wavelength is also a key factor. Currently, there are four common laser wavelengths: 650nm, 810nm, 915nm, and 980nm, each with unique characteristics.
650nm mainly targets the melanin absorption of the skin and plays a very positive role in skin tissue healing and reducing scar formation.
810nm is mainly absorbed by cytochrome c oxidase in cells, enhancing mitochondrial activity, promoting oxygen metabolism, and accelerating the production of energy molecules such as ATP, thus enhancing the metabolism and activity of the cells, and promoting cell proliferation and tissue repair.
915nm is mainly targeted at the absorption of oxygenated hemoglobin, which can promote the separation of hemoglobin and oxygen, thus improving the oxygen content of the irradiated tissues. The improvement of tissue oxygen content plays a positive role in normalizing the function of target tissues, relieving oxidative stress, and accelerating healing.
980nm mainly targets water absorption in tissues, which can accelerate the improvement of blood and lymphatic microcirculation, bring more nutrients to the lesion tissues, enhance the function of the immune system, and reduce the inflammatory reaction, all of which have very positive effects.
How to Choose the Right Laser Therapy Equipment?
Class 3B Lasers: With their specific penetration depth, Class 3B laser therapy equipment is primarily used for surface treatments and pain relief in small animals.
Class 4 Lasers: Thanks to their deeper tissue penetration capabilities, Class 4 lasers have a much wider range of applications in laser therapy and can be used for various types of animals.
Unless the laser therapy equipment is used specifically for certain diseases or specific scenarios, a multi-wavelength, high-power Class 4 laser is ideal for providing a deep and efficient treatment program that is tailored to the animal's size and treatment needs. For example, the Vaymed V-Heal and Skyline Class 4 laser therapy equipment are suitable for different scenarios. For family veterinarians or small animal specialists who mainly deal with everyday pain relief, inflammation reduction, and promoting the healing of superficial wounds, the V-Heal class 4 laser therapy device is a better fit. However, rehabilitation therapists and veterinarians handle a wide range of complex cases involving various animal species. In this case, the Skyline laser therapy equipment, with more than 1,000 built-in therapeutic options, is more applicable.
References
[1] Class 4 Laser Therapy Systems - SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Environment, Safety & Health Division
[2] Understanding the Differences Between Class III and Class IV Lasers - KEYENCE America